Risk management
Based on the principle of “Sound and Effective Corporate Governance” set forth in the CSR Charter and Code of Conduct, we have established the Risk Management Policy. In line with the policy, the SCREEN Group is engaged in initiatives aimed at identifying and mitigating business risk, and the holding company has in place a system for assessing the status of risk management for the entire Group.
Risk management structure
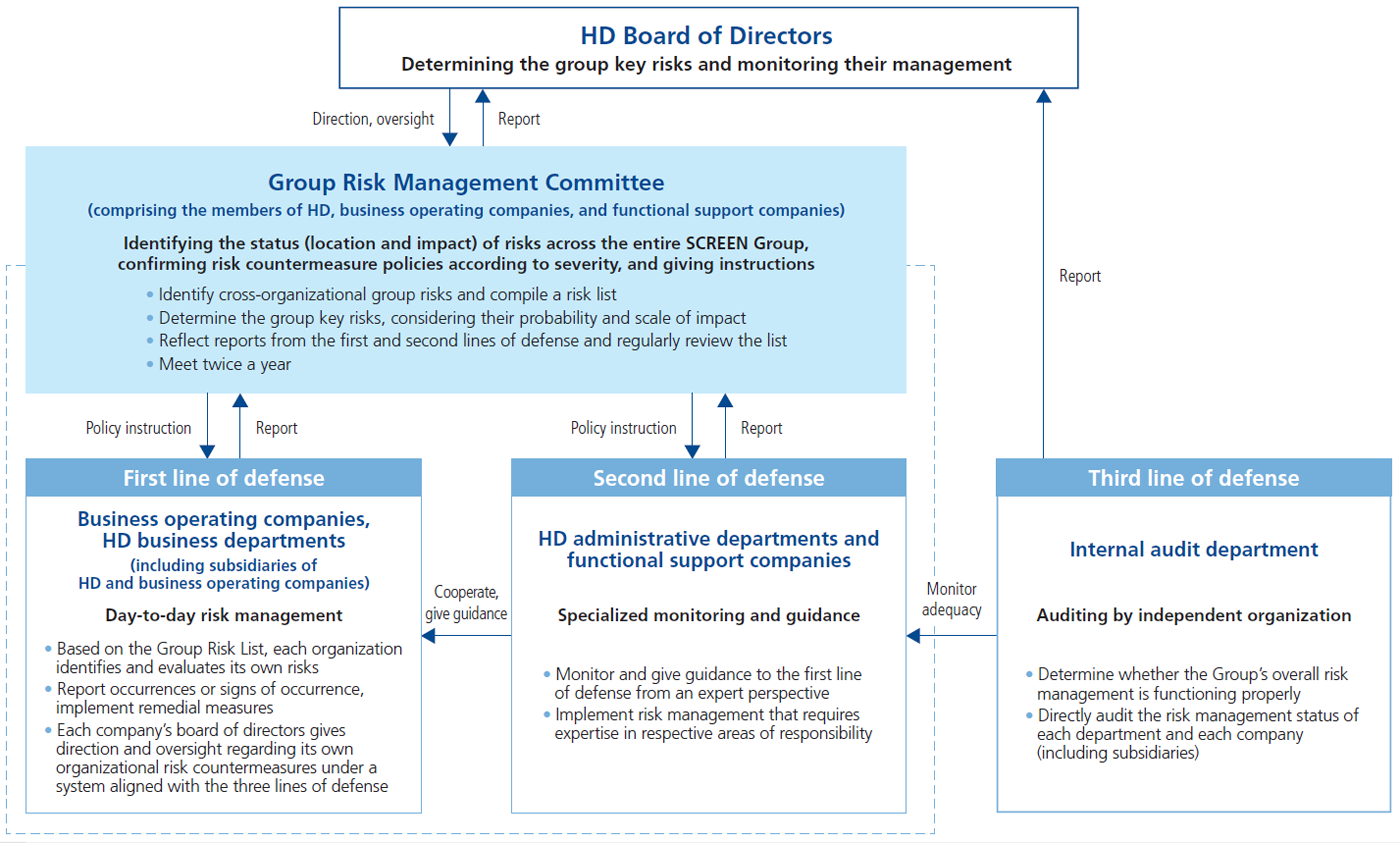
In order to mitigate risks with the potential to negatively impact the SCREEN Group’s corporate value, we have established a group-wide risk management structure headed by the SCREEN Holdings president & CEO, with the president of each group company responsible for managing risk at their own company.
The Group Risk Management Committee is at the center of this structure, conducting risk management operations, establishing risk management policies, identifying risks inherent in the entire Group, and monitoring their status with the aim of preventing and minimizing damage to corporate value. The committee also identifies group key risks in response to changes in the business environment each fiscal year to determine the direction of risk management and prevent these risks from materializing.
Group key risks are selected for the current fiscal year from among the items on the Group Risk List through discussion by the Group Risk Management Committee and finalized by resolution of the SCREEN Holdings Board of Directors. Furthermore, taking an approach built around three lines of defense,* we have designated risk managers for individual risks and their specific roles as part of a governance structure for sharing risk-related information across all levels of operations, all the way up to senior management.
* The first line of defense is borne by the group business operating companies, etc., the second line of defense by the SCREEN Holdings’ administrative departments and functional support companies, and the third line of defense by the internal audit department.
● Risk management structure and roles
Enhancing risk management effectiveness
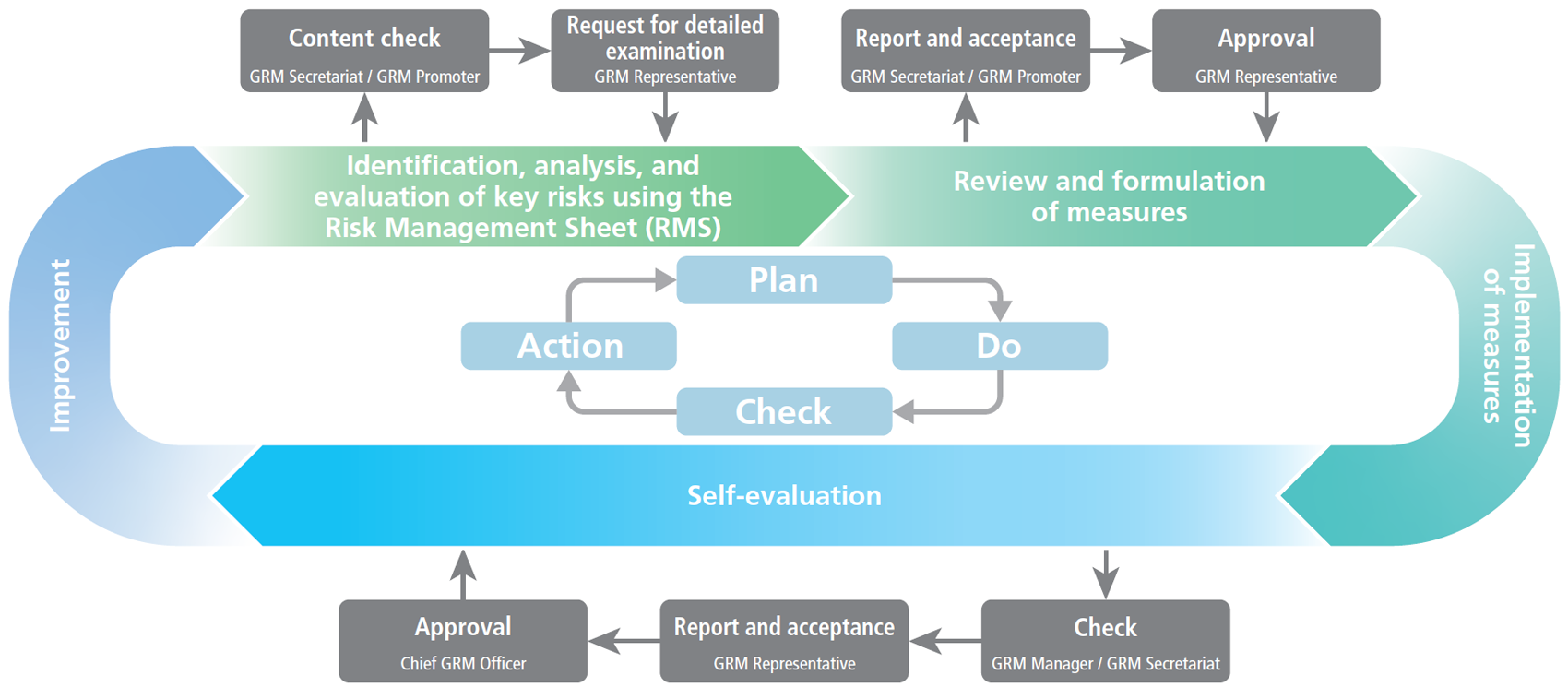
In the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025, as in the previous fiscal year, the four major business operating companies on the first line of defense and relevant members of the second line of defense held discussions, with the second line reviewing risk items, mainly group key risks, and supporting risk reduction activities. In order to apply consistent risk assessment standards throughout the Group, we established risk assessment criteria in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024. Using these criteria, we are further enhancing risk management through such efforts as discussing the appropriateness of the first line of defense’s risk assessment results, the adequacy of specific measures, and details of related support.
●Group risk management (GRM) operational flow
●Group key risks (FY2026/03)
| Risk category | Overview of Group key risks | Mitigation measure examples |
|
1. Internal control and compliance |
●Fraudulent or improper activities within the Group (e.g., inadequate internal control, insufficient or weakening of compliance awareness) |
●Review workflows and strengthen check functions ●Fully implement thoroughgoing compliance education |
|
2. Management planning, profitability |
●Sudden changes in clients’ capital investment | ●Keep updated on the progress of clients’ capital investment plans ●Develop and implement profit improvement plans, as necessary, based on monthly profit/loss forecasts |
|
3. Supply chain management (SCM) |
●Increased inventories arising from SCM or production (excess inventories of procured parts/materials, service parts, work in process, finished goods, etc.) |
●Monitor inventories through the inventory management committee ●Shorten production lead time through manufacturing transformation and reduce slow-moving inventories |
|
4. Technology and products |
●Decline in market share (delayed development of new technologies/products, weakened sales capabilities) |
●Formulate a product development strategy that accurately reflects client needs ●Develop and release products in line with the technology roadmap |
|
5. Safe working environments |
●Occupational accidents and injuries | ●Strengthen efforts to eliminate potential causes of such incidents before they occur |
|
6. Information systems and supplier management |
●Problems related to information security ●Cyberattacks on suppliers |
●Constantly monitor device operations and server processing through endpoint detection and response (EDR) ●Encrypt client information by introducing sensitivity labels ●Conduct security management surveys of major suppliers |
| 7. Development of next-generation talent | ●Decline in employee engagement | ●Analyze engagement survey results and take necessary measures ●Deepen awareness of the corporate philosophy, purpose, and creation of shared value (CSV) |
| 8. Development of next-generation leaders | ●Delays in successor development | ●Strategically develop next-generation business leaders through talent reviews ●Implement next-generation business leader development through internal training programs |
| 9. Tighter environmental regulations | ●Delays in action to reduce environmental impacts (GHG emissions from business activities/products) |
●Implement the Super Green Product certification system to reduce Scope 3 emissions ●Strategically expand the proportion of sales from Super Green Products |
Business continuity plans
The SCREEN Group strives to stay well prepared for emergencies, such as natural disasters and pandemics, with top priority placed on the safety of employees and their families. To ensure that we can continue to fulfill our responsibility to supply products and services even in the event of a catastrophic disaster, we have acquired certification under ISO 22301, an international standard for business continuity management systems, and have in place an effective system for implementing business continuity plans (BCPs) to quickly resume business operations.
Emergency system
Our safety confirmation system is designed to promptly check the safety of employees in an emergency, while our disaster information sharing system helps us grasp and share the extent of damage from a disaster quickly and accurately. We conduct regular, systematic disaster response training using these systems and comprehensive drills based on major disaster scenarios. All group companies in and outside Japan had formulated BCPs by March 31, 2024, and we held disaster drills involving overseas sites in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025. In Japan, we also enhanced and reinforced the Group’s overall emergency response capabilities by strengthening cooperation on BCPs with suppliers and conducting evacuation drills based on factory fire scenarios.
Strengthening the manufacturing base
For our operating sites in Japan, we undertake a variety of measures, including evaluating seismic resistance, reinforcing buildings, dismantling aging facilities, immobilizing equipment and facilities, and adopting seismic-resistant machinery and equipment. Based on lessons learned from past large-scale disasters and supply chain interruptions, we endeavor to put in place production systems in which production sites and parts suppliers in and outside Japan can be used to cover for one another if necessary in order to prevent significant damage to our business from such events. At the Hikone Site in Shiga Prefecture, which produces semiconductor manufacturing equipment, we have taken earthquake countermeasures and completed the installation of flood barriers. At other sites, we are advancing measures tailored to specific site characteristics, including systematic flood countermeasures.
Stable procurement
We are also reinforcing BCPs in procurement, including introducing a system to check the impact on suppliers after a disaster, finding alternatives to critical parts, and diversifying procurement sources and logistics partners. To extend these activities throughout the value chain, we are enhancing the field service structure to support clients affected by disasters and conducting surveys on suppliers’ BCP readiness.
Strengthening information security control
SCREEN regards cyberattacks and other information security risks as a key management issue. Under the leadership of SCREEN Holdings’ senior corporate strategy officer, we continuously work to strengthen information security by formulating and implementing group-wide rules and an IT roadmap, which sets forth medium- to long-term policies.
Types of cyberattacks and information security risks are evolving on a daily basis. To ensure that we can rapidly respond to these changes, we operate round-the-clock global monitoring to detect and respond to suspicious behavior on computers and servers. Recognizing that protecting information security is our social responsibility, we take measures to ensure smooth business continuity, including exercises simulating responses to potential incidents.
Moreover, we regularly review information security rules and guidelines and work to improve awareness among all employees, as well as temporary personnel and everyone working with the SCREEN Group, through such means as annual information security training with the latest information.
The SCREEN Group has established a risk management framework to strengthen information security control. Building on this, and taking a comprehensive view that encompasses risk management in the supply chain, including contractors, we are working to enhance security to comply with relevant national laws and regulations and meet industry group standards for information security.